
As companies make bolder commitments to advance diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI), stakeholders are looking for more information to back up their claims. Shareholder resolutions related to racial equity more than doubled at U.S. companies last year, many focused specifically on convincing companies to publicly disclose diversity data about their workforces.
Likewise, the vast majority of the American public — 92 percent, according to 2022 polling from Just Capital — feel it's important for companies to promote racial equity in the workplace. And they recognize data is an important tool to do it, with 76 percent of respondents to Just Capital's survey agreeing that disclosing demographic data is an important step toward advancing racial equity.
While some corporate commitments related to racial equity have failed to fully materialize, the area of diversity disclosures in particular is one where companies are stepping up in a big way, with record levels of best-practice disclosure across the world's largest public firms.
The state of corporate diversity disclosures
What's often missed in conversations about diversity disclosures is that most large companies already track this information because they're legally obligated to do so. All U.S. public companies with more than 100 employees are required to submit annual reports to the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission and Department of Labor that detail workforce data, including breakdowns by race and ethnicity, sex, and job categories.
These reports, known as EEO-1 reports, are kept confidential by government agencies unless companies choose to voluntarily disclose them — and more companies are going just that.
Nearly 75 percent of Russell 1,000 companies disclose some form of workforce diversity data, compared to 55 percent in 2021, according to tracking from Just Capital. Within that group, 34 percent of companies publicly disclosed their EEO-1 reports or similar intersectional data last year — a more than threefold increase from 11 percent a year earlier.
"Over the past year, companies across the Russell 1,000 have made great strides toward improving disclosure of racial and ethnic workforce demographic data," Just Capital's director of research insights, Matthew Nestler, and his team wrote in the report.
When Just Capital last gathered disclosure data in September 2021, nearly half of all Russell 1,000 companies made no diversity disclosures at all. By September of last year, that number had fallen to 28 percent, as more than 150 companies opted to newly disclose their diversity data.
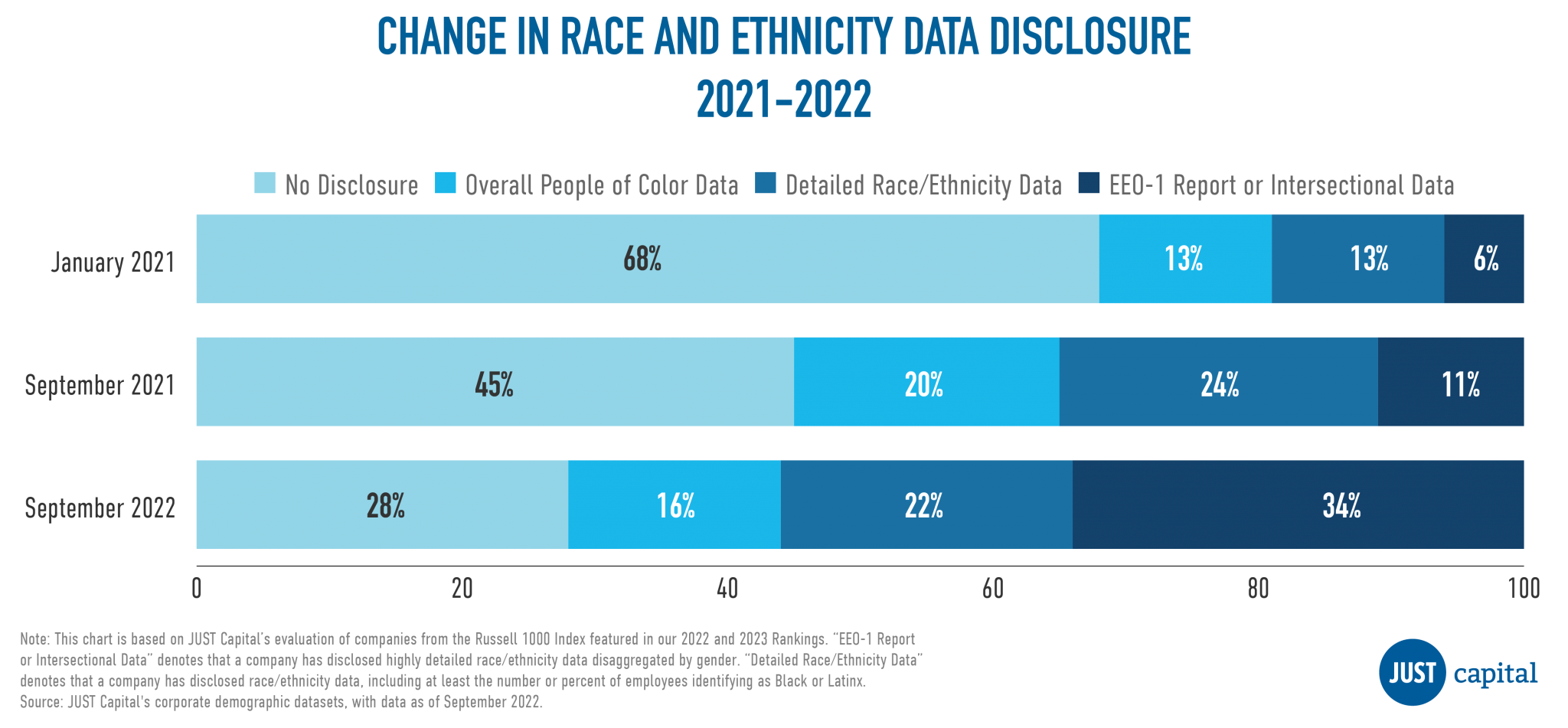
Importantly, many of these companies are skipping over the less granular disclosures, such as data about overall “non-white” or “minority” employees without racial and ethnic categories or job title breakdowns, and going right for publication of their EEO-1 reports.
Given increased stakeholder interest, it's no surprise that companies taking the lead on diversity disclosures are reaping the benefits: Companies that published their EEO-1 or similar intersectional data outperformed those that didn’t by 7.9 percent over the trailing one-year period ending in 2022, according to a companion analysis from Just Capital.
"Publicly disclosing demographic data represents a critical initial step for companies looking to build more diverse workforces, as well as stronger returns," Nestler and his team wrote in the report. "It holds corporate leaders to account on their DEI goals and signals commitment to advancing racial equity."
The bottom line
This type of rapid change indicates that advocacy from investors and consumers is working: Business leaders are hearing their stakeholders loud at clear, at least within the context of diversity disclosures. And even as anti-woke crusaders erroneously blame DEI "distractions" for everything from the Ohio train derailment to the collapse of Silicon Valley Bank, companies don't appear to be backing down.
"The story the report tells may not be a perfect one, but disclosure is a crucial first step in holding companies accountable to change," Nestler and his team concluded. "From there, to ensure lasting progress on DEI, corporate leaders must ultimately go beyond demographic disclosure and measure and disclose the outcomes of their DEI efforts, including whether C-Suite compensation is tied to DEI-related progress, what resources are directed toward DEI efforts, how they drive impact in local communities, and more."
Just Capital works to incentivize corporate behavior change on DEI issues through accountability initiatives like the Corporate Racial Equity Tracker and actionable guidance like the CEO Blueprint for Racial Equity. Other resources such as the business-led coalition CEO Action for Diversity and Inclusion, and its Actions Database of more than 1,900 insights, are also at hand to guide business leaders as they look to advance DEI within their workforces.
Image credit: August de Richelieu/Pexels

Mary has reported on sustainability and social impact for over a decade and now serves as executive editor of TriplePundit. She is also the general manager of TriplePundit's Brand Studio, which has worked with dozens of organizations on sustainability storytelling, and VP of content for TriplePundit's parent company 3BL.














